The Linux command fuser can be incredibly useful when you need to check which processes are currently using a specific file or directory. In this post, we’ll explore what the fuser command is and how to utilize its various options.
Table of Contents
What is the fuser Command?
fuser is a Linux command used to identify processes associated with a file or directory. It allows you to determine which process is using a specific file in the file system. For example, if a process is locking a file, preventing you from deleting or moving it, you can identify and terminate the process using fuser.
Basic Usage of the fuser Command
The most basic usage of the fuser command is as follows:
fuser [file or directory path]For instance, you can check which process is using the a.txt file using the following command:

Explanation of Options
The fuser command offers various options to perform more detailed operations. Below are some of the most commonly used and useful options.
-k Option: Terminate a Process
The fuser -k option forcefully terminates the processes that are using a specific file. You must use this option carefully because forcefully terminating a process can cause system or program instability.
fuser -k a.txtThis command terminates all processes using the a.txt file. The result will display only the process numbers, just like before.

However, as shown in the figure below, the application running the process will be terminated.
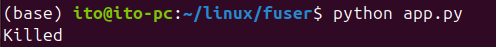
-i Option: Request Confirmation from the User
The -i option, used with -k, prompts the user for confirmation before terminating the process. This is a useful way to avoid accidentally terminating critical processes.
fuser -k -i a.txtThis command will display a message like ‘Kill process xxxxx? (y/N)’ before each process is terminated.
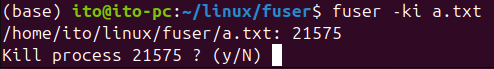
-v Option: Display Detailed Information
The -v option displays detailed information about the processes using the file. This includes not only the process ID but also the process owner, process state, and the command used to run the process.
fuser -v a.txtThis command shows detailed information about all processes using the a.txt file. The figure below shows that the file is being accessed by a Python application.
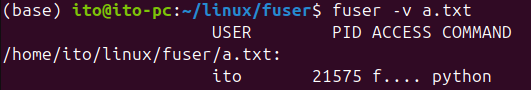
-u Option: Display User Name
The -u option displays not only the process ID but also the name of the user who started the process.
fuser -u /home/user/test.txtThis command shows both the process ID and the user name for the processes using the file.

-m Option: Check Mounted File Systems
The -m option is useful for identifying processes across an entire file system. It’s used when you want to check the processes associated with the entire file system rather than a specific file.
fuser -m /dev/stdoutThis command displays all processes using the /dev/stdout file system.

Important Considerations
The fuser command is powerful but should be used with caution. When using the -k option, be careful not to terminate critical system processes. Doing so can cause data loss or system instability. Additionally, some commands may require root privileges, so you might need to prepend sudo to the command.
sudo fuser -k /home/user/test.txtSummary
The Linux fuser command is incredibly useful for identifying which processes are using a specific file or directory. Beyond basic usage, you can leverage options to terminate processes, check user information, display detailed process information, and even investigate entire file systems. However, especially when forcefully terminating processes, be sure to use the command carefully to avoid system instability or data loss. Proper use of fuser can help resolve various system management issues effectively.
