The Linux command comm is a valuable tool that helps you easily identify the differences and similarities between two sorted files. In this post, we will explore the basic usage of the comm command and various options for its effective use. Let’s delve into how you can leverage the comm command for file comparison tasks in Linux.
Table of Contents
What is the Linux Command comm?
The comm command is a basic Linux utility that compares two sorted files and outputs the unique and common items between them. “Sorted files” here refer to files that are arranged in alphabetical or numerical order. This command is particularly useful for analyzing the similarities and differences between two files.
Why Should the Files Be Sorted?
When comparing two files, the comm command compares their contents line by line. If the files are not sorted, you will not get accurate comparison results. Therefore, it is crucial to sort the files using the sort command before using comm. Using comm on unsorted files may produce unintended outcomes.
Basic Usage of the comm Command
The basic usage of the comm command is as follows:
comm [options] file1 file2This command compares the two files and outputs the result in three columns by default:
- The first column shows the items unique to the first file.
- The second column shows the items unique to the second file.
- The third column shows the items common to both files.
Example
Let’s consider the following two files:
file1.txt:
apple
banana
cherryfile2.txt:
banana
cherry
dateNow, by using the comm command to compare these two files:
comm file1.txt file2.txtThe output will be:
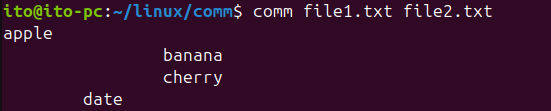
- The first column shows
apple, which is unique tofile1.txt. - The second column shows
date, which is unique tofile2.txt. - The third column shows
bananaandcherry, which are common to both files.
Key Options for the comm Command
The comm command provides various options to filter the output according to your needs. Below are some of the most commonly used options.
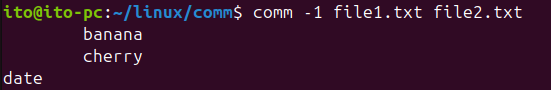
-1 Option: Hide Items Unique to the First File
This option hides the items that are unique to the first file. It is useful when you only want to see the items common to both files and the items unique to the second file.
comm -1 file1.txt file2.txtThe output will be:
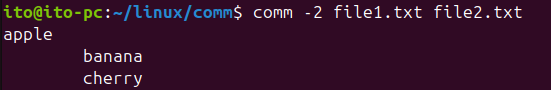
-2 Option: Hide Items Unique to the Second File
This option hides the items that are unique to the second file. It is used when you want to see the items unique to the first file and the items common to both files.
comm -2 file1.txt file2.txtThe output will be:
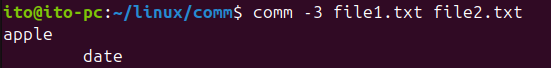
-3 Option: Hide Items Common to Both Files
This option hides the items that are common to both files. It is useful when you only want to see the differences between the two files.
comm -3 file1.txt file2.txtThe output will be:
Combining Options
The options mentioned above can be combined to filter the output even further. For instance, if you only want to see the items common to both files, you can combine the -1 and -2 options:
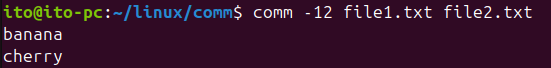
comm -12 file1.txt file2.txtThis will output:
Useful Applications
The comm command is not just limited to finding differences and similarities between two files; it can be applied in various scenarios.
Using with File Sorting
As mentioned earlier, the comm command only works correctly with sorted files. If you need to compare unsorted files, you can use the sort command to sort the files before comparing them.
sort file1.txt -o sorted_file1.txt
sort file2.txt -o sorted_file2.txt
comm sorted_file1.txt sorted_file2.txtThis ensures that the comparison is accurate.
Quickly Finding Differences Between Files
If you want to quickly find the differences between two files, you can use the -3 option to hide common items and focus on the differences. This is particularly useful in file synchronization tasks.
Using in Scripts
The comm command is extremely useful in shell scripts. For example, you can automate the comparison of two lists to determine which items have been added or removed.
new_items=$(comm -13 old_list.txt new_list.txt)
removed_items=$(comm -23 old_list.txt new_list.txt)In this script, new_items will contain the newly added items, and removed_items will contain the items that have been removed.
Precautions
When using the comm command, ensure that both files are sorted. If the files are not sorted, the command may not produce the expected results. Additionally, differences in file format or encoding can lead to incorrect comparisons, so always verify that the files are compatible for comparison.
Summary
The Linux command comm is a powerful tool for quickly identifying differences and similarities between two sorted files. By using its various options, you can filter the results to meet your needs and perform file comparison tasks more efficiently. Remember to sort your files beforehand and understand the use of each option to get the most out of this command. With the knowledge gained from this post, you should be well-equipped to use the comm command effectively in your Linux workflow.
