Linuxコマンドstatは、ファイルやディレクトリの詳細情報を確認する際に非常に有用です。この記事では、statコマンドの使い方と主要なオプション、そして実生活での活用方法について説明します。
目次
Linuxコマンドstatとは?
statコマンドは、ファイルまたはファイルシステムの状態を表示するLinuxコマンドです。ファイルのサイズ、権限、最終アクセス時間、変更時間、作成時間などの様々な情報を提供します。
基本使用法
基本的にstatコマンドを使用するには、ターミナルで次のように入力します:
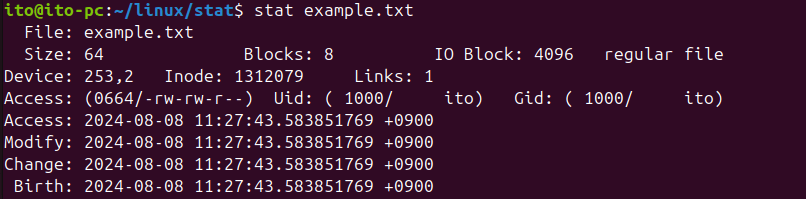
stat [filename or directory]例えば、現在のディレクトリにあるexample.txtファイルの状態を確認するには、次のように入力します:
stat example.txtこのコマンドを実行すると、次のような結果が出力されます。
主要オプション
statコマンドは様々なオプションを提供しており、必要な情報だけを選択して見ることができます。いくつかの主要オプションを見てみましょう。
-Lオプション(リンクの元ファイル)
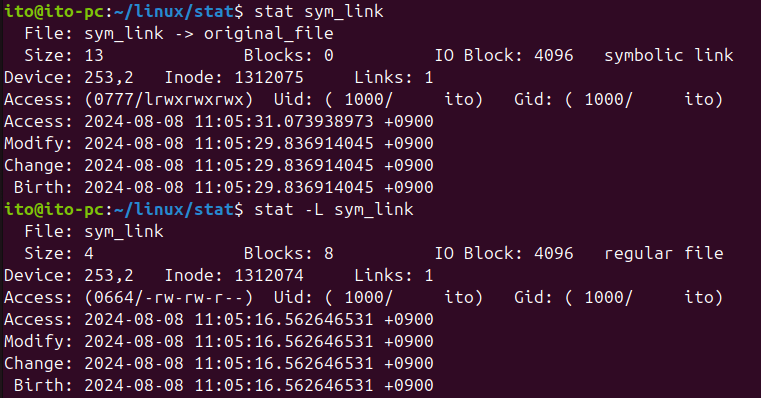
-Lオプションを使用すると、シンボリックリンクの場合、リンク自体ではなく元のファイルの情報を閲覧できます。リンクの内容を確認して元を探し出してからstatコマンドで確認する必要はなく、-Lオプションを使うことで直接元ファイルの情報を閲覧できます。
stat -L filename以下の図を見ると、-Lオプションなしでstatコマンドだけを使用した場合には、シンボリックリンクがどのように接続されているかを示し、そのファイルがシンボリックリンクであることを知らせてくれます。一方、-Lオプションを使用した場合には、元のファイルであるoriginal_fileの内容を示します。
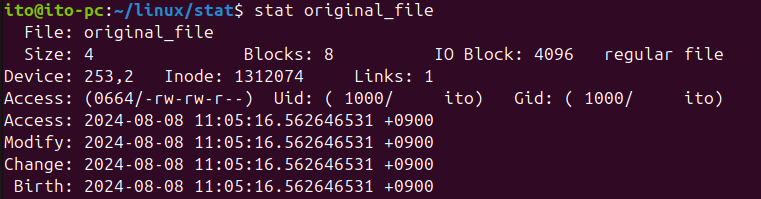
以下はoriginal_fileの情報です。上の図でstat -Lオプションを利用した場合と同じ結果であることが確認できます。
-c, –formatオプション(形式指定)
-cオプションと–formatオプションは、出力形式を指定することができます。しかし、出力フォーマット文字列にバックスラッシュと一緒に使用する特殊文字を解釈してくれません。出力の最後に改行文字(\n)が追加され、改行されて出力が終了します。
次はファイルの名前、サイズ、権限を順に示す例です。
stat -c "Name: %n Size(bytes): %s Permissions: %A" example.txtここで%nはファイル名、%sはファイルサイズを示します。結果は次のようにファイル名とファイルサイズが出力されることが確認できます。

–printfオプション
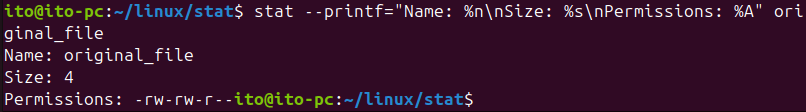
–printfオプションも-cや–formatオプションと同様にフォーマット形式を使用できます。ただし、-cオプションや–formatオプションと異なる点は、文字列フォーマットをすべて出力した後に改行をしてくれないことです。したがって、改行を望む場合は改行文字を追加する必要があります。さらに、–printfオプションを使用すると、\nや\tなどのバックスラッシュを伴う特殊文字の使用が可能です。
stat --printf="Name: %n\nSize: %s\nPermissions: %A" example.txt以下の例では改行文字を追加しなかったため、次に出てくるコマンドプロンプトがそのまま出力文字列の後に続いていることが確認できます。
-tオプション(要約形式)
-tオプションは出力結果を一行で要約して表示します。複数のファイルを簡単に比較する際に便利です。
stat -t example.txt結果は次のようになります。

上記の出力結果は以下の-cオプションを使用した場合と同じ結果です。
stat -c "%n %s %b %f %u %g %D %i %h %t %T %X %Y %Z %W %o" original_file出力フォーマットの種類
以下は出力に使用できるフォーマットです。
The valid format sequences for files (without --file-system):
%apermission bits in octal (note '#' and '0' printf flags)
%Apermission bits and file type in human readable form
%bnumber of blocks allocated (see %B)
%Bthe size in bytes of each block reported by %b
%CSELinux security context string
%ddevice number in decimal (st_dev)
%Ddevice number in hex (st_dev)
%Hdmajor device number in decimal
%Ldminor device number in decimal
%fraw mode in hex
%Ffile type
%ggroup ID of owner
%Ggroup name of owner
%hnumber of hard links
%iinode number
%mmount point
%nfile name
%Nquoted file name with dereference if symbolic link
%ooptimal I/O transfer size hint
%stotal size, in bytes
%rdevice type in decimal (st_rdev)
%Rdevice type in hex (st_rdev)
%Hrmajor device type in decimal, for character/block device special files
%Lrminor device type in decimal, for character/block device special files
%tmajor device type in hex, for character/block device special files
%Tminor device type in hex, for character/block device special files
%uuser ID of owner
%Uuser name of owner
%wtime of file birth, human-readable; - if unknown
%Wtime of file birth, seconds since Epoch; 0 if unknown
%xtime of last access, human-readable
%Xtime of last access, seconds since Epoch
%ytime of last data modification, human-readable
%Ytime of last data modification, seconds since Epoch
%ztime of last status change, human-readable
%Ztime of last status change, seconds since Epoch
Valid format sequences for file systems:
%afree blocks available to non-superuser
%btotal data blocks in file system
%ctotal file nodes in file system
%dfree file nodes in file system
%ffree blocks in file system
%ifile system ID in hex
%lmaximum length of filenames
%nfile name
%sblock size (for faster transfers)
%Sfundamental block size (for block counts)
%tfile system type in hex
%Tfile system type in human readable form
実生活での活用方法
ファイル管理およびバックアップ
ファイルの最終アクセス時間や変更時間を確認することで、ファイルがどのくらい頻繁に使用されているかを把握できます。これにより、古いファイルを整理したり、バックアップ戦略を立てたりする際に役立ちます。
スクリプト作成
Linuxコマンドstatを活用して、さまざまなスクリプトを作成できます。たとえば、特定のサイズ以上のファイルを検索してリストを出力するスクリプトを作成できます。
#!/bin/bash
for file in *
do
if [ $(stat -c %s "$file") -gt 50 ]
then
echo "$file"
fi
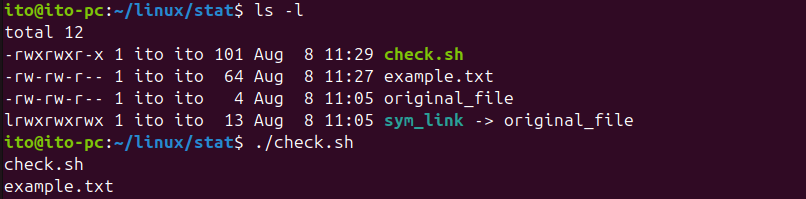
done上記のスクリプトは、現在のディレクトリ内のファイルのうち、サイズが50バイト以上のファイルを出力します。以下のファイルのうち、サイズが50バイト以上のcheck.shとexample.txtのみが出力されることを確認できます。
まとめ
statコマンドは、Linuxシステムでファイルやディレクトリの詳細情報を確認する際に非常に有用なツールです。さまざまなオプションを活用することで、必要な情報を効率的に取得でき、それによってファイル管理、スクリプト作成、システムモニタリングなど、さまざまな作業を実行できます。statコマンドを上手に活用することで、Linuxシステムをより効果的に管理できるようになるでしょう。
