When working in a Linux environment, you often need to check the current working directory’s location. The Linux command pwd is very useful in this situation. In this post, we will look at the basic usage of the Linux command pwd and some practical examples.
Table of Contents
What is the Linux Command pwd?
pwd stands for “print working directory,” and it is a command used to output the absolute path of the current working directory. It is widely used in Linux and Unix-like systems and is useful for checking the path of the current directory.
Basic Usage
When you type the pwd command, it outputs the absolute path of the current working directory. The usage is very simple.
pwdThe result of executing the Linux pwd command is shown in the image below.

pwdFrom the above example, you can see that /home/ito is the current working directory.
Useful Options
-L Option
The -L option is the default value. By default, it shows the current working directory following symbolic links.
pwd -LAs shown below, it shows the path including the symbolic link shots under /home/ito.
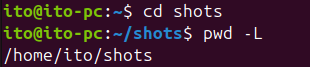
-L Option of the Linux Command pwd-P Option
The -P option displays the physical path, not the symbolic link path, when showing the current directory.
pwd -PSince the symbolic link ~/shots is used for /home/ito/Pictures/Screenshots, the actual path, not the symbolic link, is displayed in the image below.

-P Option of the Linux Command pwdWhen to Use and Purpose
The pwd command can be useful in the following situations:
- To Check Your Current Location in the File System: It helps prevent confusion about your current location when working in multiple directories.
- To Verify Working Directory in Script Writing: It’s useful for setting paths when, for example, saving log files to specific directories or performing tasks based on file paths.
Helpful Related Concepts: Absolute Path and Relative Path
An absolute path refers to the full path starting from the root of the file system. A relative path refers to the path relative to the current working directory. The pwd command outputs the absolute path, so you can clearly know your current location.
An absolute path is written starting from the root directory / as shown below:
/etc/init.d
A relative path is written based on the current directory. A single dot (.) refers to the current directory, and two dots (..) refer to the parent directory.
../../Downloads/apps
Connection with cd Command
The cd command is used to change directories. Using pwd along with cd makes it easier to navigate and confirm your location between directories.
cd Downloads
pwdYou can change the working directory using the cd command and then confirm the path with the pwd command as shown below.
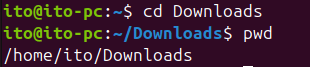
cd and pwd Commands in LinuxUsing pwd in Script Writing
When writing shell scripts, using the pwd command allows you to perform tasks based on the current directory.
#!/bin/bash
echo "Current Directory: $(pwd)"The result of writing and executing the above script is shown below.

Summary
The Linux pwd command is essential for checking the current working directory. It can be used in various situations and combined with other commands to create a more efficient working environment. If you have any additional questions or need more information, feel free to ask!
I hope this post helps you in your Linux endeavors. Happy Linuxing!
