The Linux Command which is highly useful when you need to determine where a specific command is located on your system. For instance, if commands with the same name exist in multiple directories, the which command can help you identify which path is being prioritized by the system. In this post, we will explore how to use the which command, its main options, and some practical examples.
Table of Contents
What is the Linux Command which?
The Linux Command which is a utility that finds the actual path of a command that you input. In other words, it allows you to identify the location of a particular command on your system. This is especially useful for determining which program is being executed and for preventing conflicts related to command paths.
Basic Usage
The basic usage of the which command is straightforward. You can use it as follows:
which [command name]For example, if you want to check where the python command is located, you can enter:
which pythonWhen this command is executed, the system will output the first path where an executable file named python is found within the directories defined by the PATH environment variable. The image below shows that the python file is located under the anaconda3/bin directory in the home directory.

What is the PATH Environment Variable?
To understand the which command, you need to know about the PATH environment variable. PATH is an environment variable that contains a list of directories that the shell (command interpreter) searches to find executable files when a command is run. The which command traverses these directories, as defined in PATH, in order to locate the command.
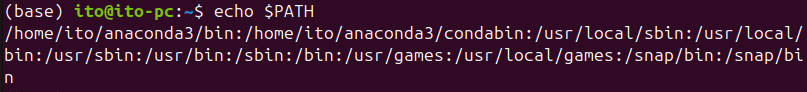
You can check the PATH variable with the following command:
echo $PATHWhen you execute this command, multiple paths separated by colons (:) will be displayed, as shown in the image below. These paths represent the order in which the shell searches for commands.
Explanation of Main Options
The which command comes with a few useful options that allow you to retrieve more detailed information.
-a Option: Show All Paths
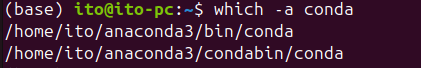
By default, the which command only outputs the first path it finds. However, using the -a option will display all the paths that contain executable files with the specified name. For example, you can use it as follows:
which -a condaThis command will display all the paths that contain an executable file named conda. If a specific command exists in multiple directories, this helps prevent conflicts or lets you verify the priority.
-s Option: Suppress Output
Sometimes, you may want to simply check whether a command exists without displaying its path. In such cases, you can use the -s option. This option suppresses the output of the path and instead returns a success code (0) if the command exists or a failure code (1) if it does not.
which -s pythonAs shown in the image below, python exists, but python5 does not.
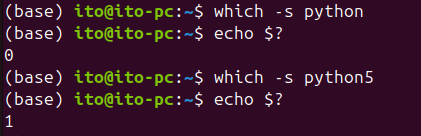
This command does not produce any output, but you can check the return code using $?. This method is particularly useful in scripts to verify whether a specific command is installed.
Practical Examples
Using in Scripts
For example, you can create a script that checks whether a specific command exists and, if not, outputs an error message and exits:
#!/bin/bash
if which -s python; then
echo "Python is installed."
else
echo "Python is not installed."
exit 1
fiThis script checks whether the python command exists and prints a message accordingly. If python is not installed, the script exits with code 1.
If python is installed, running the above script will show the following result.

Verifying Command Paths and Troubleshooting
When a program behaves unexpectedly on a Linux system, you can use the which command to check which path is being used to execute the program. For instance, if the version of a program is not what you expected, you can use which to verify the program’s path and ensure that it is the correct one.
Cautions
The which command only searches for commands within directories that are set in the PATH variable. If you want to find a command located in a directory not included in PATH, the which command will not be able to locate it. Therefore, if you are looking for a program installed in a specific directory, you should either check the PATH variable first or manually search the directory.
Additionally, which is generally used in shells like bash, zsh, etc., and its behavior may vary depending on the system environment or the user’s shell settings.
Summary
The Linux Command which is a simple yet extremely useful tool. It helps you verify command paths and check the priority when multiple versions of a program exist. It is also handy for quickly checking the existence of a command when writing scripts, helping to prevent errors. However, keep in mind that the which command is limited to searching within the PATH variable, so use it accordingly.
Now, take advantage of the which command for effective system management and script writing!
